Grade Distribution Table
In accordance with the terms of the Erasmus Charter and the ECTS User’s Guide, Utrecht Theological University has introduced the Grade Distribution Table (GDT) as of November 1, 2020. The intention is to make the results obtained transparent. We do this first of all so that the given grades/results at other institutions, branches or in other countries can be well understood and compared correctly. Thus, the GDT is not intended to assess the results of the individual student. But it is intended to provide insight into the value of grades obtained (grade culture). In addition, to make grades internationally comparable.
The Dutch grading system
The Dutch grading system, which we use from primary to university education, is a scale from 1 to 10, where 10 is the highest grade achievable and a 5.5 is the minimum to achieve a passing grade. 1 is the lowest grade. Nationwide, the custom is that a 9 or a 10 are rarely given and that a 6, a 7 and an 8 are acceptable grades, with an 8 being a really good grade.
The study load per academic year is expressed in 60 ECTS credits, where 1 credit represents a study load of 28 hours. A bachelor has a total of 180 ECTS, a master has either 60 ECTS or 180 ECTS.
Explanation of Grade Distribution Tables.
- At Utrecht Theological University, we give grades between 1 and 10 to assess an educational activity. With a 5.5 or higher, you then pass. We display the grades in the GDT in grades between 5.5 and 10.
- The tables use satisfactory grades earned in three previous college years (T-2 to T-4). These are satisfactory grades for each bachelor’s or master’s degree.
- We then express in percentages how often a particular grade was earned.
- The ‘%’ row shows the absolute percentage: how often a particular grade was given. The row ‘cum. %’ (cumulative) indicates the number of cases in which a particular grade or higher was obtained.
How can you use the Grade Distribution Table for grade conversion?
Compare the grade distribution on your diploma supplement or from your program on this website with the grade distribution developed by the other institution for a parallel reference group. We can compare the position of each grade within the two tables and convert individual grades based on this comparison.
The conversion of your grade is done per course unit by means of the so-called GDT .
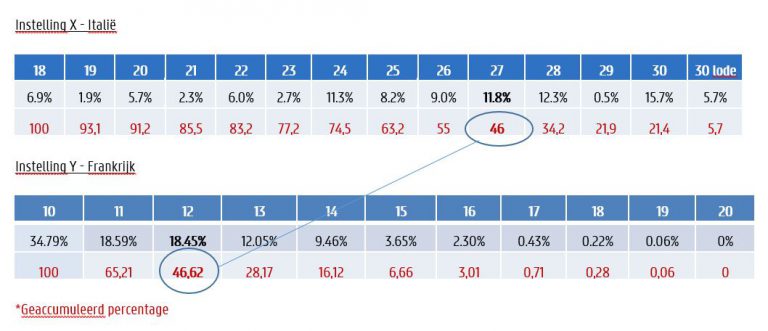
The illustration below (source: ECTS Users’ Guide) illustrates the use of Grade distribution tables when converting exam grades. In the example, the student with a grade of 27 out of 30 in a university in Italy (“X”) is among the top 46% in the reference group. To convert the point to the system of a French university, we then assume the percentile of this institution (“Y”) that best matches 46. Thus, in this case, percentile 46.62 of institution Y best matches percentile 46 of institution x and the Italian exam grade 27 is converted to a 12 at the French institution.